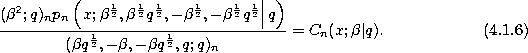Continuous dual q-Hahn.
Continuous dual q-Hahn.
 Continuous dual q-Hahn.
Continuous dual q-Hahn.
The continuous dual q-Hahn polynomials defined by (3.3.1) simply follow
from the Askey-Wilson polynomials given by (3.1.1) by setting
d = 0 in (3.1.1) :
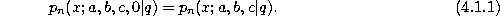
 Continuous q-Hahn.
Continuous q-Hahn.
The continuous q-Hahn polynomials defined by (3.4.1) can be obtained
from the Askey-Wilson polynomials given by (3.1.1) by the substitutions
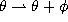 ,
, 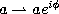 ,
, 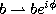 ,
,
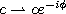 and
and 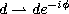 :
:
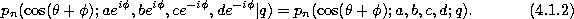
 Big q-Jacobi.
Big q-Jacobi.
The big q-Jacobi polynomials defined by (3.5.1) can be obtained from the
Askey-Wilson polynomials by setting 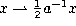 ,
, 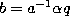 ,
,
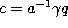 and
and 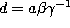 in
in
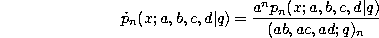
defined by (3.1.1) and then taking the limit 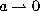 :
:
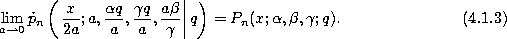
 Continuous q-Jacobi.
Continuous q-Jacobi.
If we take 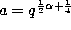 ,
, 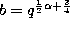 ,
,
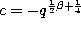 and
and 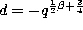 in
the definition (3.1.1) of the Askey-Wilson polynomials and
change the normalization we find the continuous q-Jacobi polynomials given
by (3.10.1) :
in
the definition (3.1.1) of the Askey-Wilson polynomials and
change the normalization we find the continuous q-Jacobi polynomials given
by (3.10.1) :
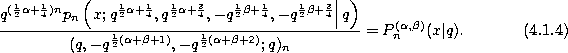
In [345] M. Rahman takes 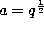 ,
,
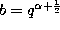 ,
, 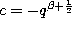 and
and
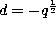 to obtain after a change of normalization the
continuous q-Jacobi polynomials defined by (3.10.14) :
to obtain after a change of normalization the
continuous q-Jacobi polynomials defined by (3.10.14) :
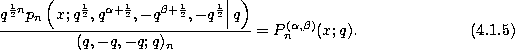
As was pointed out in section 0.6 these two q-analogues of the Jacobi polynomials are not really different, since they are connected by the quadratic transformation
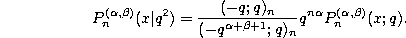
 Continuous q-ultraspherical / Rogers.
Continuous q-ultraspherical / Rogers.
If we set 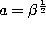 ,
, 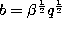 ,
,
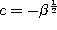 and
and 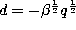 in the definition
(3.1.1) of the Askey-Wilson polynomials and change the
normalization we obtain the continuous q-ultraspherical (or Rogers)
polynomials defined by (3.10.15). In fact we have :
in the definition
(3.1.1) of the Askey-Wilson polynomials and change the
normalization we obtain the continuous q-ultraspherical (or Rogers)
polynomials defined by (3.10.15). In fact we have :